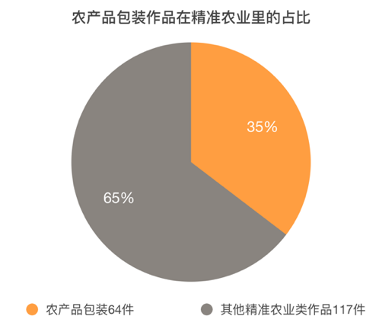
关键词:文化科技融合;现代服务业;设计
1 文化科技融合的战略意义与动力机制
1.1 文化科技融合的战略意义
1.2 文化科技支撑的动力机制
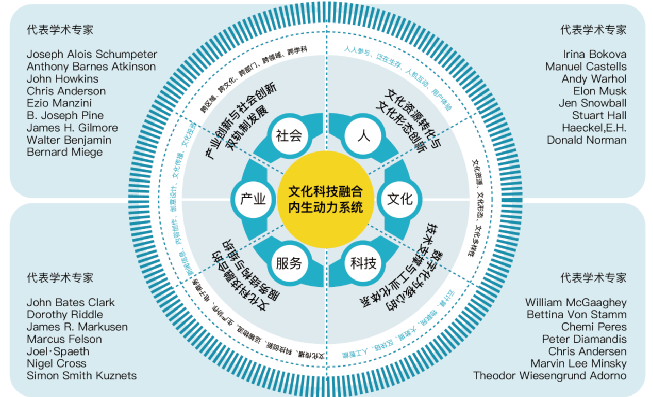
1.2.1 产业创新与社会创新的双轨制发展
图1 文化科技融合驱动的产业与社会创新系统
Fig.1 Industrial & social innovation system driven by integration of culture and technology
1.2.2 文化资源转化与文化形态创新
1.2.3 数字化为核心的技术支撑与工业化体系
1.2.4 文化科技融合的服务结构与组织
2 现代服务业的概念与行业分析
2.1 现代服务业的概念概述与发展背景
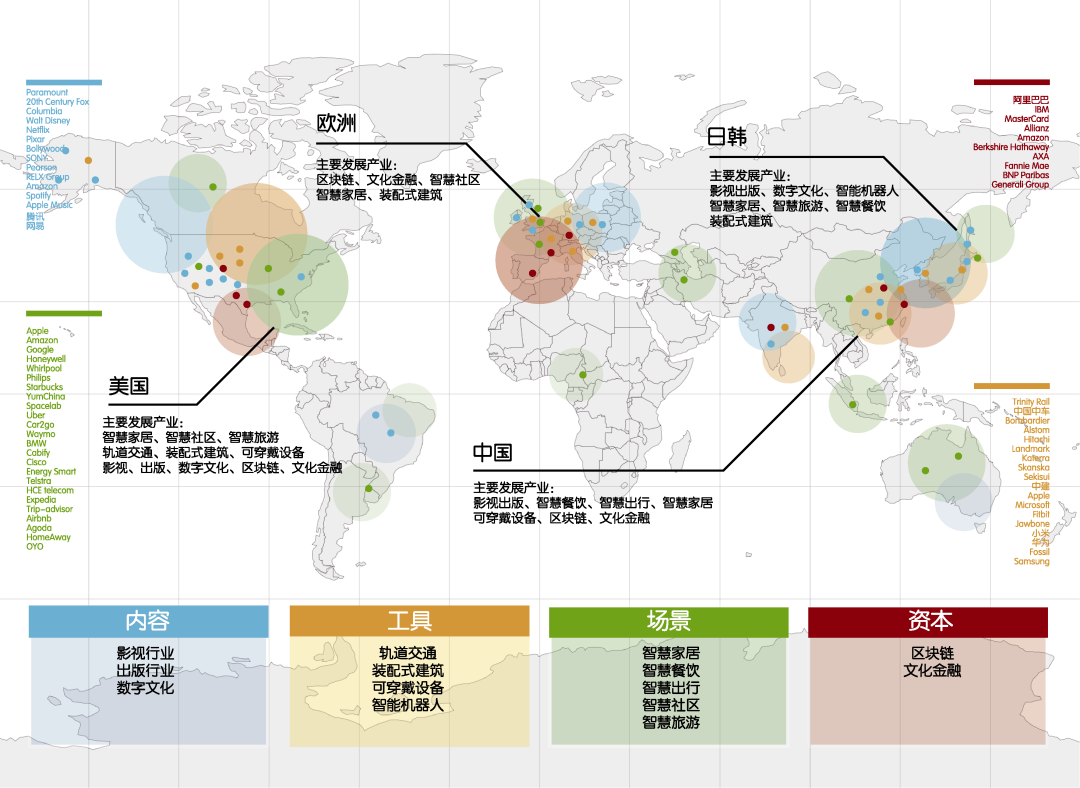
2.2 现代服务业新兴业态与科技支撑
表1 现代服务业的新兴技术与行业整理
Tab.1 Emerging technology and industry collation of modern service industry
|
分类 |
技术行业 |
产业生态 |
科技支撑 |
|
内容 |
影视行业 |
Paramount、20th Century Fox、Columbia、Walt Disney、Netflix、Pixar、Bollywood、SONY |
AR/VR/MR、4K+5G、3D影视技术、立体视效、体三维捕捉与体三维影片、基于CNN扩展网络的识别方法、三维卷积核(3D CNN)法、动作识别技术、视频结构化分析、IDT(Improved Dense Trajectories)技术、全息影像技术 |
|
出版行业 |
Pearson、RELX Group、Amazon、WILEY、Scholastic、Cengage、 |
数据挖掘、内容聚合与分发、文字识别、智能文本分类、语义识别、移动协作、智能工作空间、活动流、自动分析算法(Automated analysis algorithms)、上下文感知计算(Context-aware computing) |
|
|
数字文化 |
Spotify、AppleMusic、Amazon、腾讯、网易、Bloomberg、 |
边缘计算、机器学习、神经网络、自然语言处理、 文字识别、可视化、自动分析算法、上下文感知计算、数据挖掘技术、现代声光技术、数字耦合技术、认知计算、通用机器智能系统、分布式海量数据储存、海量数据管理技术 |
|
|
工具 |
轨道交通 |
TrinityRail、中国中车 Bombardier、Alstom、Hitachi、GETransportation |
无人驾驶、IoT物联网、车际通信、新能源、新材料、移动电力、建模与仿真、量子信息和传感技术(Quantum information and sensing technology) |
|
装配式建筑 |
Landmark、Katerra、CFCL、CDLP、Skanska、Ambercon、Sekisui、 |
智能算法、信息编码、BIM模型、RFID技术、SSGF、横向和垂直系统集成、增材制造、叠层制造、建筑信息模型、MR |
|
|
可穿戴设备 |
Apple、Microsoft、Fitbit、Jawbone、Misfit、Garmin、小米、华为、Fossil、Samsung |
云计算、场景融合、AR/VR/MR、物联网、微处理器技术、片上系统(Systems-on-Chip,SoC)、片上堆栈存储器、脑机接口(Brain-Computer Interfaces) |
|
|
智能机器人 |
Google、FANUC、Omron、EPSON、YASKAWA、Intel、KUKA、BOSCH、Staubli、大疆 |
深度学习、知识图谱、生物识别、神经网络、语音合成、微型无人机和微型机器人系统、集群技术、自动装配机器人、分子机器人、机器人编制系统、智能微尘、微处理器技术 |
|
|
场景 |
智慧家居 |
Apple、Amazon、Google、Honeywell、Whirlpool、 |
IoT、神经网络、CoSS协议、AIoT人工智能、面纹和声纹技术(Faceprint and voiceprint technologies)、片上堆栈存储器、人类机能增进、手势控制、虚拟个人助理、移动健康监测、量化自我 |
|
智慧餐饮 |
Starbucks、McDonald’s、YumChina、Costa、 |
串联农业、物联网、大数据、区块链、SaaS,自助点餐系统、手机点餐系统、KDS智能后厨显示系统、取餐叫号系统、H5动画电子餐牌、餐厅数据可视化分析 |
|
|
智慧出行 |
Uber、Car2go、Waymo、 |
自动驾驶、车联网、清洁能源、智能雷达、V2X、OTA、Position, Navigation, and Timing(PNT)、飞行控制算法、推进技术、热防护系统、专用材料、量子信息和传感技术、传感技术 |
|
|
智慧社区 |
Cisco、Energy Smart、 |
云交换平台、环境监测、气候变化技术、暂时性设交、LORA技术、RFID技术、NFC技术、OCR(光学字符识别)技术、新能源 |
|
|
智慧旅游 |
Expedia、Trip Advisor、 |
元搜索、360度虚拟景区、3D立体全景地图、VR、智能导航、地理信息系统(GIS)实时跟踪定位、电子围栏报警、SOS紧急求救、客流数据分析、全息投影、图像识别、内容分发、智能客服、景区三维街景地图、客流高峰智能预测模型、智能定价促销系统、智能推荐机制、生物识别、机器人 |
|
|
资本 |
区块链技术 |
阿里巴巴、IBM、MasterCard、Allianz、Amazon、Ciox、 |
P2P交互、哈希算法、公钥加密、分布式账本、网络编程、分布式算法、加密签名、数据存储技术、分布式存储、机器学习、VR、共识算法、钱包开发 |
|
文化金融 |
Berkshire Hathaway、AXA、Allianz、Fannie Mae、 |
移动支付、P2P、数字货币、机器学习、自然语言处理、知识图谱的构建、文本分析、文本上下供应链上的分析、智能标签系统、分布式架构开源软件、支付清算系统、现金生命周期管理 |
图2 现代服务业的新兴技术与行业地图
Fig.2 Emerging technology and industry map of modern service industry
3 文化科技融合的现代服务业创新发展趋势
3.1 泛在生存、全民娱乐与IP化
3.2 万物互联、双向感知的文化消费体验
3.3 人人参与、脑机融合的赋能设计与平台化运营
3.4 文旅融合与智慧旅游
3.5 双向互动的文化生产、教育学习
3.6 分享经济与文化消费的爆发
3.7 文化金融引领的商业模式创新与产业升级
4 创意经济下的文化产业生态
4.1 创意经济与文化产业
4.2 文化产业的理论发展
表2 文化产业的理论发展
Tab.2 Theoretical development of cultural industries
|
分期 |
阶段 |
时间 |
代表组织 |
代表人物 |
代表理论 |
|
认识期 |
思辨批判阶段 |
20世纪30年代 |
法兰克福学派 |
瓦尔特·本雅明 |
文化生产 |
|
西奥多·阿多诺 |
文化工业 |
||||
|
评断期 |
洞悉反思阶段 |
20世纪60年代 |
伯明翰学派 |
斯图亚特·霍尔 |
大众文化 |
|
认可期 |
融合创新阶段 |
20世纪80年代 |
欧洲议会文化 合作委员会 |
伯纳德·米亚基 |
文化产业 |
4.2.1 文化产业理论的认识期
4.2.2 文化产业理论的评断期
4.2.3 文化产业理论的认可期
4.3 文化产业生态的研究体系
5 工业设计驱动的文化科技融合
5.1 设计参与的角色定位
5.2 人工智能时代工业设计的发展趋势
5.2.1 将人工智能作为设计资源
5.2.2 从产品设计到服务系统设计
5.2.3 从造型设计到交互体验设计
5.2.4 从基于直觉的设计到数据驱动的设计
5.2.5 从人机设计到人与智能体关系的设计
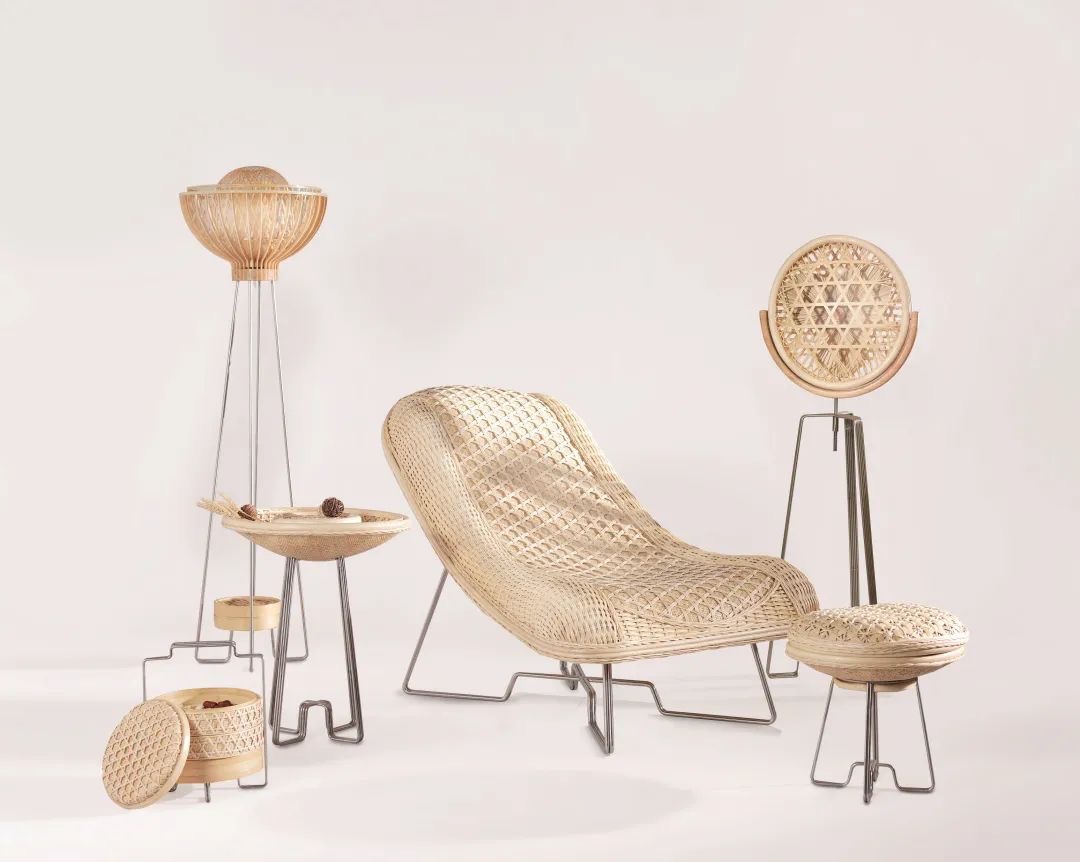
5.3 工业设计驱动的文化科技融合发展思路
6 结语
参考文献:
[1]陈劲, 尹西明. 中国科技创新与发展2035展望[J]. 科学与管理, 2019, 39(1): 1—7.
CHEN Jin, YIN Xi-ming. Outlook of China’s Technology Innovation and Development 2035[J]. Science and Management, 2019, 39(1): 1—7.
[2]威廉·麦克高希. 世界文明史: 观察世界的新视角[M]. 北京: 新华出版社, 2003.
MCGAAGHEY W. Five Epochs of Civilization: World History as Emerging in Five Civilizations[M]. Beijing: Xinhua Publishing House, 2003.
[3]刘琦岩. 推进科技与文化深度融合支撑引领文化产业发展[J]. 甘肃科技, 2012, 28(1): 1—2.
LIU Qi-yan. Promoting the Deep Integration of Technology and Culture, Support and Lead the Development of Cultural Industry[J]. Gansu Science and Technology, 2012, 28(1): 1—2.
[4]STAMM B V. Innovation—What’s Design Got to Do with It?[J]. Design Management Review, 2010, 15(1): 10—19.
[5]柯丽敏. 文化对科技创新发展的推动作用分析[J]. 科技管理研究, 2007, 27(9): 31—33.
KE Li-min. Analysis of the Promoting Role of Culture in the Development of Scientific and Technological Innovation[J]. Science and Technology Management Research, 2007, 27(9): 31—33.
[6]林秀琴. 文化科技融合的趋势及问题研究[J]. 文化产业研究, 2019(1): 116—127.
LIN Xiu-qin. The Trend and Existing Problems of Cultural and Technological Integration Innovation[J]. Cultural Industry Research, 2019(1): 116—127.
[7]花建. 迈向世界文化强国: 新里程·新动能·新地缘[J]. 中华文化论坛, 2018(3): 4—14.
HUA Jian. Towards a World Cultural Power: New Mileage, New Energy and New Geography[J]. Forum on Chinese Culture, 2018(3): 4—14.
[8]齐勇锋, 吴莉. 特色文化产业发展研究[J]. 中国特色社会主义研究, 2013, 1(5): 90—96.
QI Yong-feng, WU Li. Characteristic Cultural Industry Development Research[J]. Studies on the Socialism With Chinese Characteristics, 2013, 1(5): 90—96.
[9]安金明. 产业创新的层次性与影响因素研究[J]. 企业技术进步, 2007(11): 23—24.
AN Jin-ming. Hierarchy and Influencing Factors of Industrial Innovation Research[J]. Technological Development of Enterprise, 2007(11): 23—24.
[10]ANDERSON C. Makers: The New Industrial Revolution[M]. New York: Random House, 2012.
[11]CASTELLS M. Rise of the Network Society: The Information Age: Economy, Society and Culture[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Publishers, 1996.
[12]花建, 田野. 数字游戏产业上市企业的发展驱动力——以上海为重点的研究[J]. 深圳大学学报(人文社会科学版), 2018, 35(2): 37—47.
HUA Jian, TIAN Ye. Driving Force for the Development of Listed Digital Game Companies: a Case Study of Shanghai[J]. Journal of Shenzhen University (Humanities & Social Sciences), 2018, 35(2): 37—47.
[13]蒋友燏, 闵晓蕾. 基于乡村文化资源的内生创意系统[J]. 装饰, 2018(4): 34—38.
JIANG You-yu, MIN Xiao-lei. Endogenous Creative System Based on Rural Cultural Resources[J]. Zhuangshi, 2018(4): 34—38.
[14]CLARK J B. Essentials of Economic Theory[M]. Auburn: Ludwig Von Mises Institute, 2013.
[15]AKHTER H. Service-Led Growth: The Role of the Service Sector in World Development by Dorothy I. Riddle[J]. Journal of Marketing, 1987, 51(2): 135.
[16]MARKUSEN J R. Trade in Producer Services and in Other Specialized Intermediate Inputs[J]. The American Economic Review, 1989: 85—95.
[17]夏德元. 移动互联网时代的泛在生存与在场的缺席[J]. 新闻大学, 2016(5): 61—66.
XIA De-yuan. The Ubiquitous Existence and Absence of Presence in the Mobile Internet Era[J]. Journalism Bimonthly, 2016(5): 61—66.
[18]DIAMANDIS P H, KOTLER S. Bold: How to Go Big, Create Wealth, and Impact the World[M]. New York: Simon & Schuster, 2015.
[19]EVANS D. Social Media Marketing: An Hour a Day[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2010.
[20]李俊楼, 张骏, 马卫, 等. “互联网+” 时代下乡村旅游 O2O 融合发展及对策分析[J]. 电子商务, 2016 (10): 4—5.
LI Jun-lou, ZHANG Jun, MA Wei, et al. The Development and Countermeasures of Rural Tourism O2O Integration in the Era of “Internet+”[J]. E-Business Journal, 2016 (10): 4—5.
[21]李俊楼, 张骏, 马卫, 等. “互联网+” 时代下乡村旅游 O2O融合发展及对策分析[J]. 电子商务, 2016(10): 4—5.
LI Jun-lou, ZHANG Jun, MA Wei, et al. The Development and Countermeasures of Rural Tourism O2O Integration in the Era of “Internet+”[J]. E-Business Journal, 2016 (10): 4—5.
[22]VILPPONEN A, WINTER S, SUNDQVIST S. Electronic Word-of-mouth in Online Environments: Exploring Referral Networks Structure and Adoption Behavior[J]. Journal of Interactive Advertising, 2006, 6(2): 8—77.
[23]张新红, 高太山, 于凤霞, 等. 中国分享经济发展报告: 现状, 问题与挑战, 发展趋势[J]. 电子政务, 2016(4): 11—27.
ZHANG Xin-hong, GAO Tai-shan, YU Feng-xia, et al. China Shares Economic Development Report: Current Situation, Problems and Challenges, Development Trend[J]. E-Government, 2016 (4): 11—27.
[24]范周. 创新驱动公共文化服务体系现代化探析[J]. 现代传播(中国传媒大学学报), 2015, 37(5): 55—60.
FAN Zhou. Innovation Drives the Modernization of Public Cultural Service System[J]. Modern Communication, 2015, 37(5): 55—60.
[25]陈少峰, 李源. 文化产业的十种商业模式创新[J]. 中国国情国力, 2016(12): 14—16.
CHEN Shao-feng, LI Yuan. Ten Business Model Innovations in Cultural Industry[J]. China National Conditions and Strength, 2016(12): 14—16.
[26]花建. “一带一路”战略与提升中国文化产业国际竞争力研究[J]. 同济大学学报(社会科学版), 2016, 27(5): 30—39.
HUA Jian. On the Promotion of International Competitiveness of China’s Cultural Industry in the Background of the Belt and Road Strategy[J]. Tongji University Journal Social Science Section, 2016, 27(5): 30—39.
[27]ATKINSON A B. The Economics of the Welfare State[J]. American Economist, 1996, 40(2): 5—15.
[28]HOWKINS J. The Creative Economy: How People Make Money from Ideas[M]. London: Penguin UK, 2002.
[29]ADORNO T W, HORKHEIMER M. Dialectic of Enlightenment[M]. London: Verso, 1997.
[30]ADORNO T W, RABINBACH A G. Culture Industry Reconsidered[J]. New German Critique, 1975(6): 12— 19.
[31]苑捷. 当代西方文化产业理论研究概述[J]. 马克思主义与现实, 2004(1): 98—105.
YUAN Jie. A Summary of Contemporary Western Cultural Industry Theory Research[J]. Marxism & Reality, 2004(1): 98—105.
[32]MIEGE B, MIAEGE B. The Capitalization of Cultural Production[M]. New York: International General, 1989.
[33]J·H·斯图尔德, 玉文华. 文化生态学的概念和方法[J]. 民族译丛, 1988(6): 1—7.
STUART J H, YU Wen-hua. The Concept and Method of Cultural Ecology[J]. Min Yicong, 1988(6): 1-7.
[34]司马云杰. 关于文化建构价值意识的学说[J]. 天津社会科学, 1988(5): 60—65.
SIMA Yun-jie. Theory about Cultural Construction Value Consciousness[J]. Tianjin Social Sciences, 1988(5): 60—65.
[35]CROSS N. Designerly Ways of Knowing[J]. Design Studies, 1982, 3(4): 221—227.
[36]柳冠中. 设计: 人类未来不被毁灭的“第三种智慧”[J]. 设计艺术研究, 2011, 1(1): 1—5.
LIU Guan-zhong. Design: The “Third Wisdom” of the Undestroyed Future of Human Beings[J]. Design Research, 2011, 1(1): 1—5.
[37]LUCCHIO L D, 陈欣. 设计学的全新挑战——从对单一技术的闭门造车到学科间的协调与整合[J]. 创意与设计, 2011(4): 44—48.
LUCCHIO L D, CHEN Xin. The New Challenge of Design Discipline: From an Autarky of Skills to a Synergy Between Knowledge[J]. Creativity and Design, 2011(4): 44—48.
[38]KEA E A. The Impact of Culture on Creativity, Study Prepared for the European Commission[J]. European Commission, 2009.
[39]季铁, 潘英. 基于社区和网络的设计与社会创新——从UCD到CCD[J]. 装饰, 2012(12): 109—111.
JI Tie, PAN Ying. Community and Network Based Design and Social Innovation: From UCD to CCD[J]. Zhuangshi, 2012(12): 109—111.
[40]路甬祥, 孙守迁, 张克俊. 创新设计发展战略研究[J]. 机械设计, 2019, 36(2): 1—4.
LU Yong-xiang, SUN Shou-qian, ZHANG Ke-jun. Research on Development Strategy of Innovation Design[J]. Journal of Machine Design, 2019, 36(2): 1—4.
[41]SATO K, 刘优幽. 系统的设计方法: 构建以人为本——访美国著名设计师Keiichi Sato[J]. 设计艺术研究, 2013, 3(5): 121—124.
SATO K, LIU You-you. Systems Approach to Design: Constructing Human: Centered Design Methodology, an Interview with Designer Keiichi Sato[J]. Design Research, 2013, 3(5): 121—124.
[42]NORMAN D A. Emotional Design: Why We Love (or Hate) Everyday Things[M]. New York: Basic Civitas Books, 2004.
[43]李国杰, 程学旗. 大数据研究: 未来科技及经济社会发展的重大战略领域——大数据的研究现状与科学思考[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2012, 27(6): 647—657.
LI Guo-jie, CHENG Xue-qi. Research Status and Scientific Thinking of Big Data[J]. Strategy & Policy Decision Research, 2012, 27(6): 647—657.
[44]SING M P. Multiagent Systems: a Theoretical Framework for Intentions, Know-How, and Communications[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1994.